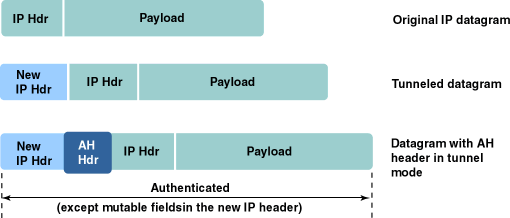
In tunnel mode, the IP datagram is the payload of a new IP
datagram. This mode is used whenever either end of a
security association is a gateway. So, if a connection is made
between two firewalls, the tunnel mode is always used.
In tunnel mode the outer headers' IP addresses do not need
to be the same as the inner headers' addresses. For example, two
security gateways can operate an AH tunnel, which is used to authenticate
all traffic between the networks they connect together. Hosts are
not required to support tunnel mode, but often they do.
The advantages of the tunnel mode are total protection of the
encapsulated IP datagram and the possibility of using private
addresses. However, there is an extra processing overhead associated
with this mode.
Figure 2