| | |
| IPSec Tunneling I | page 2 of 4 |
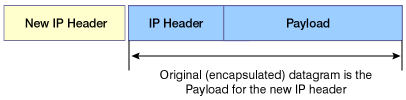
Figure 3 shows how tunneling wraps a packet into
a new one. The entire packet is treated as a payload, and a new
header attached. In IPSec, IP is tunneled through IP. This protects
the header of the encapsulated packet. By encrypting a packet,
its destination address can be concealed. This can be used, for
example, to protect internal network addresses without requiring
NAT services to be present. Figure 3
|













